Study Identifies Hundreds of Potential Targets for Cancer Drugs
Updated: 2024-10-15 19:47:11
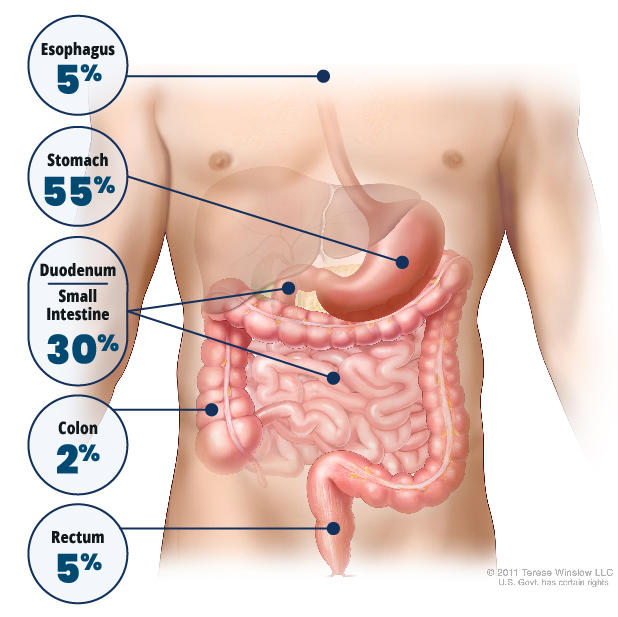 Trial participants who stopped imatinib had a more rapid worsening of disease, a shorter time until resistance, and did not live as long as participants who continued the therapy uninterrupted.
Trial participants who stopped imatinib had a more rapid worsening of disease, a shorter time until resistance, and did not live as long as participants who continued the therapy uninterrupted.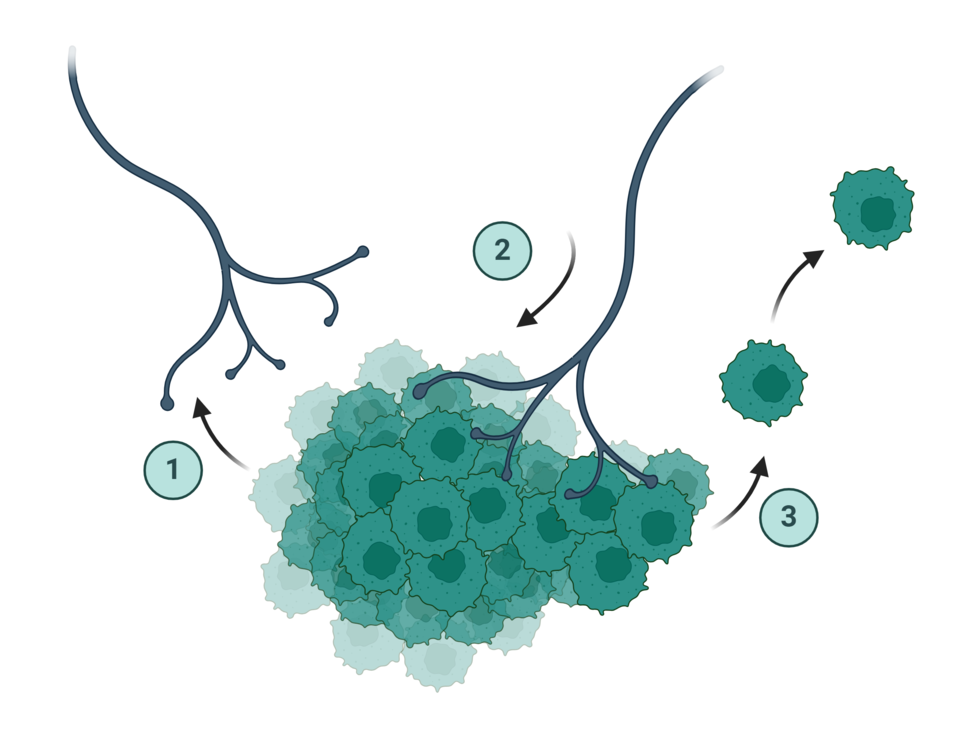 A new study may provide important new insights into breast cancer metastasis. Blood vessels within tumors release a molecule that draws sensory nerves closer to the tumors, the study shows. This close proximity turns on genes in the cancer cells that drive metastasis.
A new study may provide important new insights into breast cancer metastasis. Blood vessels within tumors release a molecule that draws sensory nerves closer to the tumors, the study shows. This close proximity turns on genes in the cancer cells that drive metastasis.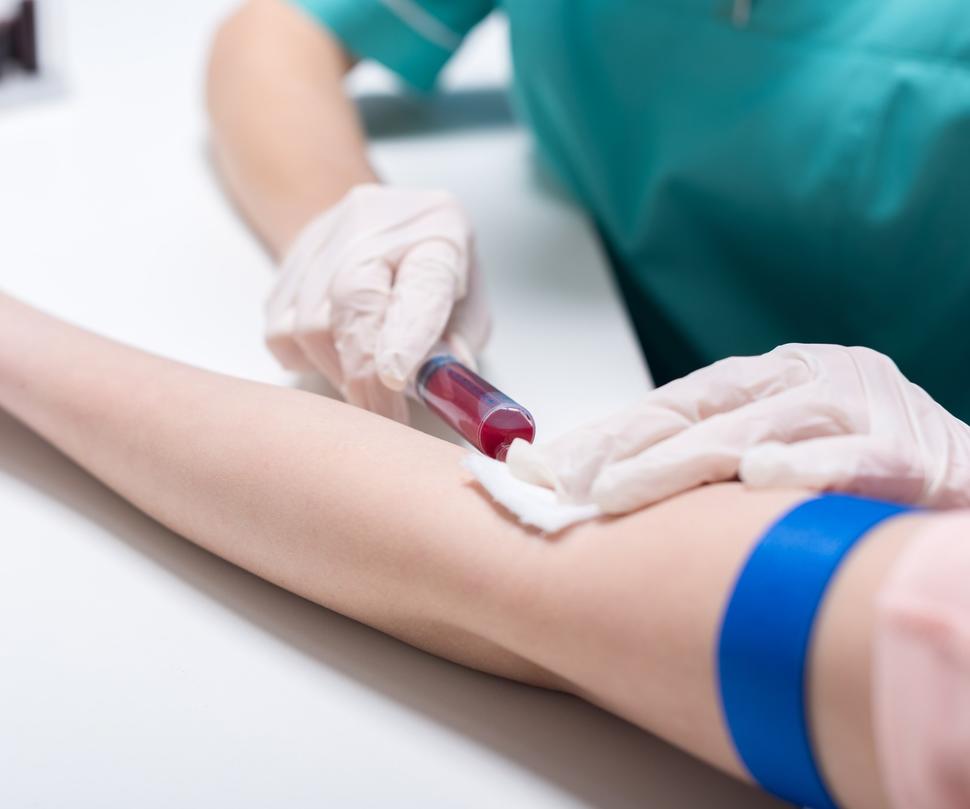 FDA recently approved the Shield test, the first blood test for the primary screening of people at average risk of colorectal cancer. Where does it fit in with other screening options for the disease, including colonoscopy and stool tests?
FDA recently approved the Shield test, the first blood test for the primary screening of people at average risk of colorectal cancer. Where does it fit in with other screening options for the disease, including colonoscopy and stool tests? Results from a French clinical trial have identified what experts say should now be the recommended initial treatment of advanced leiomyosarcoma. In the trial, the combination of trabectedin (Yondelis) and doxorubicin improved survival by a median of 9 months.
Results from a French clinical trial have identified what experts say should now be the recommended initial treatment of advanced leiomyosarcoma. In the trial, the combination of trabectedin (Yondelis) and doxorubicin improved survival by a median of 9 months.